0. 前言
在前一文[linux内存管理] 第19篇 buddy分配器基础知识以及分配器api接口中,对buddy分配器的基础知识做了简单的介绍,包括涉及到的分配掩码、分配标志、分配入口函数、释放入口函数,而buddy分配的工作是分为 快速分配和 慢速分配两种的
快速分配:指现有的buddy系统中的 free_list中有足够的内存,可以满足申请的需要,或者是通过简单的迁移就能达成申请内存的目的。
慢速分配:指中间经历了内存碎片整理、内存回收、OOM等耗时的操作,而这些操作只是为了让buddy系统获得足够的空闲内存。
注意:
正如前文我们所提到的分配函数 alloc_pages、alloc_page以及 get_zeroed_page函数追本溯源之后,可以知道都可以溯源到 alloc_page,所以本章将会以 alloc_pages函数开始剖析buddy的分配算法
1. alloc_pages函数剖析
static inline struct page *alloc_pages(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order)
{
return alloc_pages_node(numa_node_id(), gfp_mask, order);
}
static inline struct page *alloc_pages_node(int nid, gfp_t gfp_mask,
unsigned int order)
{
if (nid == NUMA_NO_NODE)
nid = numa_mem_id();
return __alloc_pages_node(nid, gfp_mask, order);
}
static inline struct page *
__alloc_pages_node(int nid, gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order)
{
VM_BUG_ON(nid < 0 || nid >= MAX_NUMNODES);
VM_WARN_ON((gfp_mask & __GFP_THISNODE) && !node_online(nid));
return __alloc_pages(gfp_mask, order, nid, NULL);
}
1.1 __alloc_pages函数剖析
struct page *__alloc_pages(gfp_t gfp, unsigned int order, int preferred_nid,
nodemask_t *nodemask)
{
struct page *page;
///允许在低水位分配内存
unsigned int alloc_flags = ALLOC_WMARK_LOW;
gfp_t alloc_gfp; /* The gfp_t that was actually used for allocation */
///ac, 用于保存伙伴系统分配内存时的参数
struct alloc_context ac = { };
/*
* There are several places where we assume that the order value is sane
* so bail out early if the request is out of bound.
*/
///伙伴系统分配最大内存块2^(max_order-1),默认4MB
if (unlikely(order >= MAX_ORDER)) {
WARN_ON_ONCE(!(gfp & __GFP_NOWARN));
return NULL;
}
// gfp_allowed_mask是一个全局掩码,表示允许的gfp mask
gfp &= gfp_allowed_mask;
/*
* Apply scoped allocation constraints. This is mainly about GFP_NOFS
* resp. GFP_NOIO which has to be inherited for all allocation requests
* from a particular context which has been marked by
* memalloc_no{fs,io}_{save,restore}. And PF_MEMALLOC_PIN which ensures
* movable zones are not used during allocation.
*/
// 此步骤是为了确保当前内存分配的上下文能够被正确的继承
gfp = current_gfp_context(gfp);
alloc_gfp = gfp;
// 来准备分配页面的上下文,填充 ac 和 alloc_flags,并根据需要调整 gfp。
if (!prepare_alloc_pages(gfp, order, preferred_nid, nodemask, &ac,
&alloc_gfp, &alloc_flags))
return NULL;
/*
* Forbid the first pass from falling back to types that fragment
* memory until all local zones are considered.
*/
///内存碎片化的一个优化,优先从高端zone分配内存
alloc_flags |= alloc_flags_nofragment(ac.preferred_zoneref->zone, gfp);
/* First allocation attempt */
///从伙伴系统的空闲链表分配内存
page = get_page_from_freelist(alloc_gfp, order, alloc_flags, &ac);
if (likely(page))
// 分配成功直接跳转out退出
// 快速分配就到此为止
goto out;
alloc_gfp = gfp;
ac.spread_dirty_pages = false;
/*
* Restore the original nodemask if it was potentially replaced with
* &cpuset_current_mems_allowed to optimize the fast-path attempt.
*/
ac.nodemask = nodemask;
///get_page_from_freelist分配不成功,进入慢速路径
page = __alloc_pages_slowpath(alloc_gfp, order, &ac);
out:
if (memcg_kmem_enabled() && (gfp & __GFP_ACCOUNT) && page &&
unlikely(__memcg_kmem_charge_page(page, gfp, order) != 0)) {
__free_pages(page, order);
page = NULL;
}
trace_mm_page_alloc(page, order, alloc_gfp, ac.migratetype);
return page;
}
我们可以看到此函数的功能分为了快速分配以及慢速分配,快速分配是通过函数 get_page_from_freelist从伙伴系统的空闲链表直接分配内存,而慢速分配则是通过 __alloc_pages_slowpath进行分配。
1.2 prepare_alloc_pages
用以确定 gfp_mask 是否设置了 __GFP_CMA ,如果设定该标记,则表示 允许 CMA 内存区域中分配内存 ,此时将 alloc_flags 添加上 ALLOC_CMAstatic inline bool prepare_alloc_pages(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order,
int preferred_nid, nodemask_t *nodemask,
struct alloc_context *ac, gfp_t *alloc_gfp,
unsigned int *alloc_flags)
{
///计算zoneidx,表示允许内存分配的最高zoneidx
ac->highest_zoneidx = gfp_zone(gfp_mask);
///指向首选内存节点对应的zonelist
ac->zonelist = node_zonelist(preferred_nid, gfp_mask);
///内存节点掩码
ac->nodemask = nodemask;
///迁移类型
ac->migratetype = gfp_migratetype(gfp_mask);
//如果启用了 cpusets,则向 alloc_gfp 添加 __GFP_HARDWALL 标志。cpusets 是 Linux 中的一种资源隔离机制,__GFP_HARDWALL 表示硬性限制内存分配在特定的节点上。
if (cpusets_enabled()) {
*alloc_gfp |= __GFP_HARDWALL;
/*
* When we are in the interrupt context, it is irrelevant
* to the current task context. It means that any node ok.
*/
if (in_task() && !ac->nodemask)
ac->nodemask = &cpuset_current_mems_allowed;
else
*alloc_flags |= ALLOC_CPUSET;
}
//分别用于获取和释放文件系统回收的上下文。这与内存分配的 gfp_mask 相关,可能是为了确保在分配过程中不干扰文件系统操作。
fs_reclaim_acquire(gfp_mask);
fs_reclaim_release(gfp_mask);
//如果 gfp_mask 中包含 __GFP_DIRECT_RECLAIM 标志,则调用 might_sleep_if。这表明当前分配可能会导致直接回收内存,因此在这种情况下,函数可能会进入睡眠状态等待内存回收。
might_sleep_if(gfp_mask & __GFP_DIRECT_RECLAIM);
if (should_fail_alloc_page(gfp_mask, order))
return false;
//用以确定 gfp_mask 是否设置了 __GFP_CMA ,如果设定该标记,则表示 允许 CMA 内存区域中分配内存 ,此时将 alloc_flags 添加上 ALLOC_CMA
*alloc_flags = gfp_to_alloc_flags_cma(gfp_mask, *alloc_flags);
/* Dirty zone balancing only done in the fast path */
//表示此次申请是否允许将该页块标记为 dirty,该值只会用于快速分配中
ac->spread_dirty_pages = (gfp_mask & __GFP_WRITE);
/*
* The preferred zone is used for statistics but crucially it is
* also used as the starting point for the zonelist iterator. It
* may get reset for allocations that ignore memory policies.
*/
//记录此次分配最受欢迎的 zoneref,该函数最开始会根据 gfp_mask 优先确定可以选择分配的 zone 的high_zoneidx,函数最后会根据该 hign_zonidx 确定zoneref
ac->preferred_zoneref = first_zones_zonelist(ac->zonelist,
ac->highest_zoneidx, ac->nodemask);
return true;
}
2. 快速分配
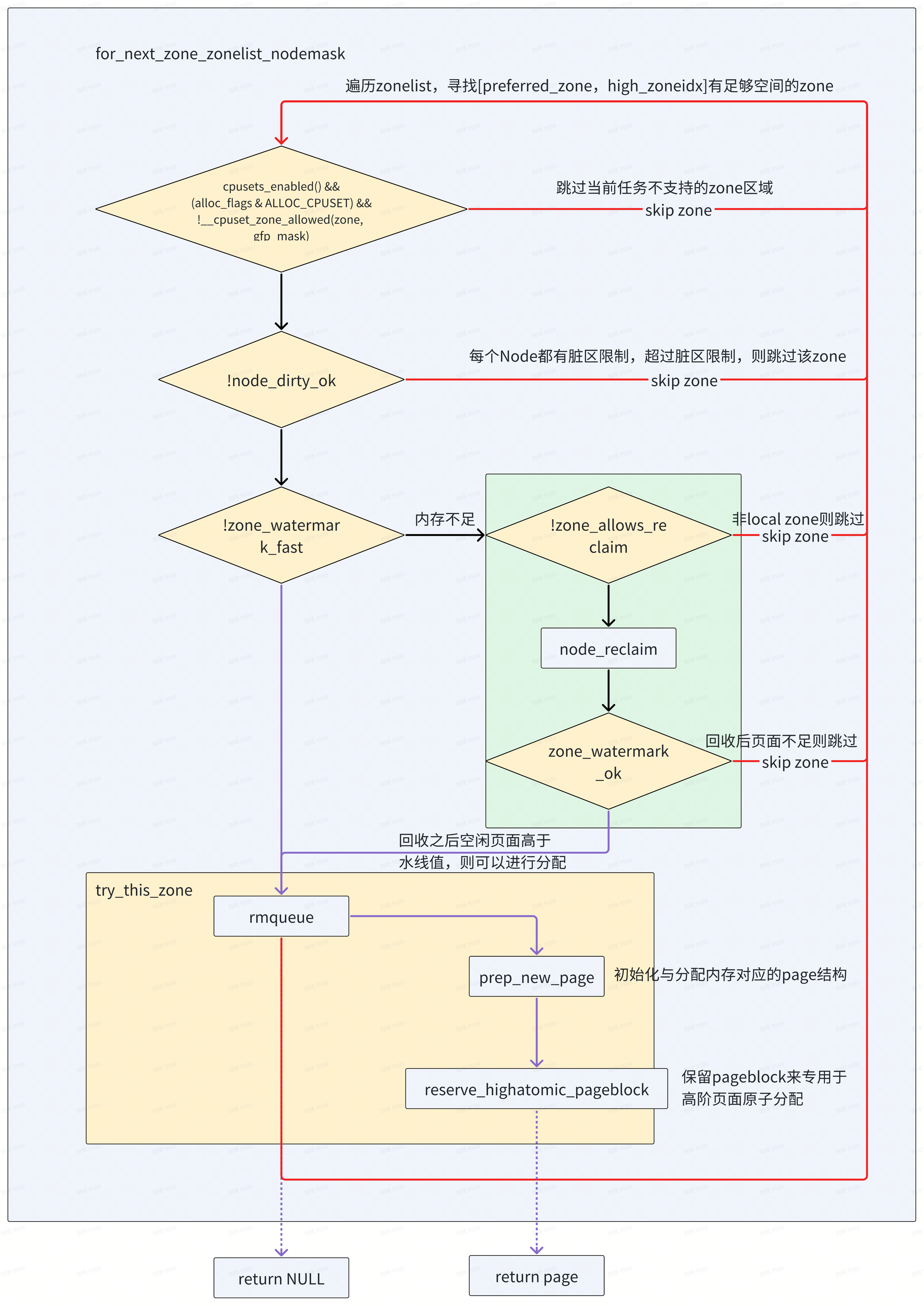
快速分配的函数入口为 get_page_from_freelist
static struct page *
get_page_from_freelist(gfp_t gfp_mask, unsigned int order, int alloc_flags,
const struct alloc_context *ac)
{
struct zoneref *z;
struct zone *zone;
struct pglist_data *last_pgdat_dirty_limit = NULL;
bool no_fallback;
retry:
/*
* Scan zonelist, looking for a zone with enough free.
* See also __cpuset_node_allowed() comment in kernel/cpuset.c.
*/
///ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT,避免内存碎片化的一个优化
no_fallback = alloc_flags & ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT;
///z,首选zone
z = ac->preferred_zoneref;
///从推荐的zone开始遍历zonelist中所有zone
for_next_zone_zonelist_nodemask(zone, z, ac->highest_zoneidx,
ac->nodemask) {
struct page *page;
unsigned long mark;
if (cpusets_enabled() &&
(alloc_flags & ALLOC_CPUSET) &&
!__cpuset_zone_allowed(zone, gfp_mask))
continue;
/*
* When allocating a page cache page for writing, we
* want to get it from a node that is within its dirty
* limit, such that no single node holds more than its
* proportional share of globally allowed dirty pages.
* The dirty limits take into account the node's
* lowmem reserves and high watermark so that kswapd
* should be able to balance it without having to
* write pages from its LRU list.
*
* XXX: For now, allow allocations to potentially
* exceed the per-node dirty limit in the slowpath
* (spread_dirty_pages unset) before going into reclaim,
* which is important when on a NUMA setup the allowed
* nodes are together not big enough to reach the
* global limit. The proper fix for these situations
* will require awareness of nodes in the
* dirty-throttling and the flusher threads.
*/
if (ac->spread_dirty_pages) {
if (last_pgdat_dirty_limit == zone->zone_pgdat)
continue;
if (!node_dirty_ok(zone->zone_pgdat)) {
last_pgdat_dirty_limit = zone->zone_pgdat;
continue;
}
}
///NUMA系统中,优先考虑的是内存节点本地性,而不是碎片化,
///本地内存速度远大于远端内存
if (no_fallback && nr_online_nodes > 1 &&
zone != ac->preferred_zoneref->zone) {
int local_nid;
/*
* If moving to a remote node, retry but allow
* fragmenting fallbacks. Locality is more important
* than fragmentation avoidance.
*/
local_nid = zone_to_nid(ac->preferred_zoneref->zone);
///判定访问远程zone,跳过,重试
if (zone_to_nid(zone) != local_nid) {
alloc_flags &= ~ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT;
goto retry;
}
}
///当检测到有外碎片化倾向时,临时提高低水位,提前触发kswapd线程回收内存,
//然后触发kcompacted做内存规整,这样有助于分配到大内存;
//
//无法分配到连续大内存,就认为有碎片化倾向,会从其他迁移类型挪用内存
mark = wmark_pages(zone, alloc_flags & ALLOC_WMARK_MASK);
///返回true,表示满足最低水位,且满足分配要求
///条件分支内容,为处理分配失败
if (!zone_watermark_fast(zone, order, mark,
ac->highest_zoneidx, alloc_flags,
gfp_mask)) {
int ret;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEFERRED_STRUCT_PAGE_INIT
/*
* Watermark failed for this zone, but see if we can
* grow this zone if it contains deferred pages.
*/
if (static_branch_unlikely(&deferred_pages)) {
if (_deferred_grow_zone(zone, order))
goto try_this_zone;
}
#endif
/* Checked here to keep the fast path fast */
BUILD_BUG_ON(ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS < NR_WMARK);
if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS)
goto try_this_zone;
///node_refclain_mode=0,表示可以从下一个zone或内存节点分配内存
//否则,就在本地zone进行一些内存回收动作
//
// /proc/sys/kernel/vm/zone_reclaim_mode影响该值,默认关闭,直接从本地zone回收内存
if (!node_reclaim_enabled() ||
!zone_allows_reclaim(ac->preferred_zoneref->zone, zone))
continue;
///尝试回收一部分内存
ret = node_reclaim(zone->zone_pgdat, gfp_mask, order);
switch (ret) {
case NODE_RECLAIM_NOSCAN:
/* did not scan */
continue;
case NODE_RECLAIM_FULL:
/* scanned but unreclaimable */
continue;
default:
/* did we reclaim enough */
if (zone_watermark_ok(zone, order, mark,
ac->highest_zoneidx, alloc_flags))
goto try_this_zone;
continue;
}
}
///马上从这个zone开始分配内存
try_this_zone:
///rmqueue,伙伴系统分配内存核心函数
page = rmqueue(ac->preferred_zoneref->zone, zone, order,
gfp_mask, alloc_flags, ac->migratetype);
if (page) {
///分配成功,设置页面属性,refcount=1,private=0等
prep_new_page(page, order, gfp_mask, alloc_flags);
/*
* If this is a high-order atomic allocation then check
* if the pageblock should be reserved for the future
*/
if (unlikely(order && (alloc_flags & ALLOC_HARDER)))
reserve_highatomic_pageblock(page, zone, order);
return page;
} else {
#ifdef CONFIG_DEFERRED_STRUCT_PAGE_INIT
/* Try again if zone has deferred pages */
if (static_branch_unlikely(&deferred_pages)) {
if (_deferred_grow_zone(zone, order))
goto try_this_zone;
}
#endif
}
}
/*
* It's possible on a UMA machine to get through all zones that are
* fragmented. If avoiding fragmentation, reset and try again.
*/
if (no_fallback) {
///遍历完所有zone之后,还是没成功分配,有可能发生了外碎片化,重试一次
alloc_flags &= ~ALLOC_NOFRAGMENT;
goto retry;
}
return NULL;
}
函数重要变量:
gfp_mask:内存分配标志。order:要求的内存块大小,以2^order的方式表示。alloc_flags:其他分配标志。ac:包含内存分配上下文的结构体,包含内存分配的各种参数(如首选的内存区域、迁移类型等)。z:指向内存区域(zone)列表的指针。zone:当前要尝试分配内存的内存区域。last_pgdat_dirty_limit:用于缓存上次分配时涉及的pgdat,用于避免重复检查。no_fallback:表示是否避免内存碎片化的优化标志。
考虑到 get_page_from_freelist() 函数涉及的逻辑比较多,本文将细节进行 拆分剖析
2.1 for_next_zone_zonelist_nodemask
include/linux/mmzone.h
#define for_next_zone_zonelist_nodemask(zone, z, zlist, highidx, nodemask) \
for (zone = z->zone; \
zone; \
z = next_zones_zonelist(++z, highidx, nodemask), \
zone = zonelist_zone(z))
通过一个for 循环,轮询不大于 highidx 的所有的 zone。
需要注意:
- alloc_context 都是来源于 __alloc_pages_nodemask() 函数;
- 在get_page_from_freelist() 函数中,该for循环中的 zone 是从 preferred_zoneref 开始轮询;
{% u 对于一个UMA 架构只有 ZONE_NORMAL 和 ZONE_DMA32 来说,优先选择分配的 zone 应该是NORMAL %}。
2.2 __cpuset_zone_allowed
mm/page_alloc.c
if (cpusets_enabled() &&
(alloc_flags & ALLOC_CPUSET) &&
!__cpuset_zone_allowed(zone, gfp_mask))
continue;
对于快速分配,prepare_alloc_pages() 函数中,当确定 cpuset 使能时会设置 alloc_mask 和alloc_flags,alloc_mask 添加上 __GFP_HARDWALL,强制使能 cpuset 内存分配策略,alloc_flags 添加上 ALLOC_CPUSET 标记位。
对于慢速分配,alloc_flags 会调用 gfp_to_alloc_flags() 重新确定,该函数这里暂时不做剖析
另外,还会通过 __cpuset_zone_allowed() 函数进一步确认该 node 是否加入到了cpuset,如果没有直接跳到下一个zone。
2.3 ac->spread_dirty_pages
当申请内存时,gfp_mask 如果设定了 __GFP_WRITE,那么caller 打算将这一页设定为 dirty,但是系统不希望每个脏页都从一个 zone 分配,所以每个node 的脏页都是有limit 的,当想要申请脏页达到 limit 或者是想要从node 中连续申请脏页是不被允许的(node 中的每个zone 都不允许)。
mm/page_alloc.c
if (ac->spread_dirty_pages) {
if (last_pgdat_dirty_limit == zone->zone_pgdat)
continue;
if (!node_dirty_ok(zone->zone_pgdat)) {
last_pgdat_dirty_limit = zone->zone_pgdat;
continue;
}
}
当 gfp_mask 设定了 __GFP_WRITE 时,该变量会被置 true。当然,spread_dirty_pages 这个变量只会用于快速分配中,{% wavy 在进入慢速分配之前,该变量的值会被强制置为 false。%}
另外,这里用了个临时变量 last_pgdat_dirty_limit 记录上一个达到 limit 的 node,如果申请内存的 zone 为此node,不会再让申请 dirty 页。
last_pgdat_dirty_limit 的初始值为 NULL,需要经过 node_dirty_ok() 确定该node 的脏页是否达到了limit:
- 如果已经申请脏页 nr_pages 还没有达到 limit,是可以继续在该node 中申请的;
- 如果达到了limit 的上限,则会记录下该node,如果发现下一个zone 的node 是 last,则直接跳过;
{% tip warning %}
注意:
对于 UMA 架构来说,node 只有一个,如果该 node 申请的脏页已经达到了 limit,则不会再允许从该 node 中分配脏页。又因为该类申请,只针对快速分配。
也就是说,对于 UMA 架构,当想要分配脏页,但已经达到了极限,那么快速分配时肯定失败的。
{% endtip %}
2.3.1 node_dirty_ok
mm/page-writeback.c
bool node_dirty_ok(struct pglist_data *pgdat)
{
unsigned long limit = node_dirty_limit(pgdat);
unsigned long nr_pages = 0;
nr_pages += node_page_state(pgdat, NR_FILE_DIRTY);
nr_pages += node_page_state(pgdat, NR_WRITEBACK);
return nr_pages <= limit;
}
static unsigned long node_dirty_limit(struct pglist_data *pgdat)
{
unsigned long node_memory = node_dirtyable_memory(pgdat);
struct task_struct *tsk = current;
unsigned long dirty;
if (vm_dirty_bytes)
dirty = DIV_ROUND_UP(vm_dirty_bytes, PAGE_SIZE) *
node_memory / global_dirtyable_memory();
else
dirty = vm_dirty_ratio * node_memory / 100;
if (rt_task(tsk))
dirty += dirty / 4;
return dirty;
}
先,通过 node_dirty_limit() 函数来统计系统脏页的极限,这里涉及到两个节点变量:
- dirty_bytes, 系统允许的脏页大小,默认为0;
- dirty_ratio, 系统允许的脏页比例,默认为20;
也就是系统中 node 的脏页极限值为 dirtyable * dirty_ratio / 100,其中dirtyable 为可以变成脏页的内存大小。
接着,统计该 node 中 NR_FILE_DIRTY 和 NR_WRITEBACK,确定是否超过 limit。
2.4 zone_watermark_fast
mm/page_alloc.c
mark = wmark_pages(zone, alloc_flags & ALLOC_WMARK_MASK);
if (!zone_watermark_fast(zone, order, mark,
ac_classzone_idx(ac), alloc_flags,
gfp_mask)) {
int ret;
在进入快速分配之前,水位会被初始化为低水位
unsigned int alloc_flags = ALLOC_WMARK_LOW;
首先通过 wmark_pages() 得到水位,此水位是加上zone 的 watermark_boost:
#define wmark_pages(z, i) (z->_watermark[i] + z->watermark_boost)
接下来通过 zone_watermark_fast() 函数判断当前 zone 的空闲页面是否满足 alloc_flags 指定的水位。
/*
* 检测判断zone是否大于最低水位,且根据order判断是否有足够大空闲内存
* 水位值在初始化时,根据空闲页面设定,也可以在节点/proc/sys/vm/mim_free_kbytes设置,kswapd内核线程也会用到
*
* z:检测是否满足请求的zone
* order:分配2^order个物理页面
* mark:要测试的水位标准;
* highest_zoneidx:首选zone的编号
* alloc_flags:属性标志位
* fgp_mask:属性屏蔽位
* */
static inline bool zone_watermark_fast(struct zone *z, unsigned int order,
unsigned long mark, int highest_zoneidx,
unsigned int alloc_flags, gfp_t gfp_mask)
{
long free_pages;
///获取zone空闲页面数量
free_pages = zone_page_state(z, NR_FREE_PAGES);
/*
* Fast check for order-0 only. If this fails then the reserves
* need to be calculated.
*/
///针对申请单个page,做快速优化
//lowmem_reserve是每个zone预留的内存,为防止高端zone在内存不足时,过度使用低端zone内存资源
if (!order) {
long fast_free;
fast_free = free_pages;
fast_free -= __zone_watermark_unusable_free(z, 0, alloc_flags);
if (fast_free > mark + z->lowmem_reserve[highest_zoneidx])
return true;
}
///进一步检查
if (__zone_watermark_ok(z, order, mark, highest_zoneidx, alloc_flags,
free_pages))
return true;
/*
* Ignore watermark boosting for GFP_ATOMIC order-0 allocations
* when checking the min watermark. The min watermark is the
* point where boosting is ignored so that kswapd is woken up
* when below the low watermark.
*/
///针对申请单个页面,进一步检查, 忽略临时水位
if (unlikely(!order && (gfp_mask & __GFP_ATOMIC) && z->watermark_boost
&& ((alloc_flags & ALLOC_WMARK_MASK) == WMARK_MIN))) {
mark = z->_watermark[WMARK_MIN];
return __zone_watermark_ok(z, order, mark, highest_zoneidx,
alloc_flags, free_pages);
}
return false;
}
这个函数有 6 个参数:
- z:表示检测是否满足分配请求的zone;
- order:需要分配物理页面的order;
- mark:表示要测试的水位大小;
- classzone_idx:表示首选 zone 的index;
- alloc_flags:分配器内存使用的标志位;
- gfp_mask:从__alloc_pages_nodemask() 中传入到 get_page_from_freelist();
注意这个函数中有个重要的数据:zone->lowmem_reserve,这个是此zone 在作为备选zone 进行分配内存时,需要预留给自己zone 使用的内存。
函数共分三大块:
- 优先考虑 order 为0 的内存申请,如果order 0 的申请都无法满足,那系统肯定存在内存紧张;
- 如果order 0 无法满足,调用 __zone_watermark_ok() 函数根据 alloc_flags 来减少水位要求;
- 如果 __zone_watermark_ok() 无法通过,那基本上就无法满足水位要求了。但系统会对 order 0 的申请,再做一次尝试,但这个条件是比较苛刻的;
2.4.1 zone_page_state
static inline unsigned long zone_page_state(struct zone *zone,
enum zone_stat_item item)
{
long x = atomic_long_read(&zone->vm_stat[item]);
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
if (x < 0)
x = 0;
#endif
return x;
}
每个zone 都有vm_stat 数组,里面存放着 zone 中各种页面的统计数据,包括空闲页面数量 NR_FREE_PAGES、NR_ZONE_INACTIVE_ANON、NR_ZONE_ACTIVE_ANON、NR_ZONE_INACTIVE_FILE、NR_ZONE_ACTIVE_FILE 等。
这里统计的是 zone 的 free_pages。
2.4.2 __zone_watermark_unusable_free
static inline long __zone_watermark_unusable_free(struct zone *z,
unsigned int order, unsigned int alloc_flags)
{
const bool alloc_harder = (alloc_flags & (ALLOC_HARDER|ALLOC_OOM));
long unusable_free = (1 << order) - 1;
/*
* If the caller does not have rights to ALLOC_HARDER then subtract
* the high-atomic reserves. This will over-estimate the size of the
* atomic reserve but it avoids a search.
*/
if (likely(!alloc_harder))
unusable_free += z->nr_reserved_highatomic;
#ifdef CONFIG_CMA
/* If allocation can't use CMA areas don't use free CMA pages */
if (!(alloc_flags & ALLOC_CMA))
unusable_free += zone_page_state(z, NR_FREE_CMA_PAGES);
#endif
return unusable_free;
}
通过 ALLOC_HARDER、ALLOC_OOM、ALLOC_CMA 确定不让使用的page,最终的free page 在计算的时候都要减掉这部分的内存。
2.4.3 __zone_watermark_ok
bool __zone_watermark_ok(struct zone *z, unsigned int order, unsigned long mark,
int highest_zoneidx, unsigned int alloc_flags,
long free_pages)
{
long min = mark;
int o;
const bool alloc_harder = (alloc_flags & (ALLOC_HARDER|ALLOC_OOM));
/* free_pages may go negative - that's OK */
free_pages -= __zone_watermark_unusable_free(z, order, alloc_flags);
if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_HIGH)
min -= min / 2;
if (unlikely(alloc_harder)) {
/*
* OOM victims can try even harder than normal ALLOC_HARDER
* users on the grounds that it's definitely going to be in
* the exit path shortly and free memory. Any allocation it
* makes during the free path will be small and short-lived.
*/
if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_OOM)
min -= min / 2;
else
min -= min / 4;
}
/*
* Check watermarks for an order-0 allocation request. If these
* are not met, then a high-order request also cannot go ahead
* even if a suitable page happened to be free.
*/
if (free_pages <= min + z->lowmem_reserve[highest_zoneidx])
return false;
/* If this is an order-0 request then the watermark is fine */
if (!order)
return true;
/* For a high-order request, check at least one suitable page is free */
///检查是否有满足oder需求的内存块
for (o = order; o < MAX_ORDER; o++) {
struct free_area *area = &z->free_area[o];
int mt;
if (!area->nr_free)
continue;
///从MIGRATE_UNMOVABLE到MIGRATE_RECLAIMABLE类型,发现符合order分配需求,就初步判断满足条件
//后续可以从迁移类型中挪用
for (mt = 0; mt < MIGRATE_PCPTYPES; mt++) {
if (!free_area_empty(area, mt))
return true;
}
#ifdef CONFIG_CMA
if ((alloc_flags & ALLOC_CMA) &&
!free_area_empty(area, MIGRATE_CMA)) {
return true;
}
#endif
if (alloc_harder && !free_area_empty(area, MIGRATE_HIGHATOMIC))
return true;
}
return false;
}
z:表示内存区域(zone)的指针。order:表示请求的内存块的大小。高阶内存请求的order大于 0。mark:表示内存水位值,用于决定是否满足分配条件。highest_zoneidx:表示允许的最高内存区域索引。alloc_flags:表示内存分配的标志,如是否高优先级(ALLOC_HIGH)或是否处理 OOM(ALLOC_OOM)。free_pages:表示当前区域内的空闲页面数量。
首先通过 __zone_watermark_unusable_free()计算出 unusable 的pages,将free pages 减掉这部分pages。
下面的逻辑是 __zone_watermark_ok() 核心:
if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_HIGH)
min -= min / 2;
- 如果
alloc_flags中设置了ALLOC_HIGH标志,表示高优先级的内存分配请求,要求更严格的水位条件。因此,减少min的值。
如果设置了 ALLOC_HARDER 或 ALLOC_OOM 标志,表示在内存紧张的情况下,分配请求可以"更加努力"。ALLOC_OOM 表示当前的请求来自于 OOM(内存不足)处理流程,通常这种情况下,内存分配会更宽松一些。
- 如果是 OOM 分配,进一步降低水位的要求(减半
min)。
- 如果只是
ALLOC_HARDER,则仅将水位减小四分之一。
2.5 ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS
如果 zone_watermark_fast() 返回false,即此次分配无法满足水位需求,会确定 此时申请是否不用关注水位情况:
if (alloc_flags & ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS)
goto try_this_zone;
alloc_flags 如果设定了 ALLOC_NO_WATERMARKS,则不用关注水位情况。
2.6 node_reclaim
如果 zone_watermark_fast() 返回false,会确定是否进入直接回收流程。
if (node_reclaim_mode == 0 ||
!zone_allows_reclaim(ac->preferred_zoneref->zone, zone))
continue;
ret = node_reclaim(zone->zone_pgdat, gfp_mask, order);
node_reclaim_mode 是个全局变量,可以通过节点 /proc/sys/vm/zone_reclaim_mode 获取,称为 zone_reclaim_mode 模式。通常情况下 zone_reclaim_mode 模式是关闭的(RECLAIM_OFF),即默认情况下关闭直接从本地 zone 进行内存回收。
另外,从内核代码上得知,对于 UMA 架构来说, node_reclaim() 是不生效的,并返回 NODE_RECLAIM_NOSCAN:
mm/internal.h
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
extern int node_reclaim(struct pglist_data *, gfp_t, unsigned int);
#else
static inline int node_reclaim(struct pglist_data *pgdat, gfp_t mask,
unsigned int order)
{
return NODE_RECLAIM_NOSCAN;
}
#endif
3. 伙伴系统内存分配核心函数rmqueue
/*
* 伙伴系统分配内存的核心函数
*
* *preferred_zone:首选的zone
* *zone: 当前遍历的zone
* order: 分配2^order个连续物理页面
* gfp_t gfp_flags:调用者传入的分配掩码
* alloc_flags: 分配器使用的标志位
* int migratetype:分配内存的迁移类型
*/
static inline
struct page *rmqueue(struct zone *preferred_zone,
struct zone *zone, unsigned int order,
gfp_t gfp_flags, unsigned int alloc_flags,
int migratetype)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct page *page;
///处理单个页的分配,
//每个zone都有个Per-CPU变量per_cpu_pages,该数据结构有一个单页面链表,
//当申请分配单个页面时,从这个物理链表直接获取,可以减少对锁的依赖;
if (likely(pcp_allowed_order(order))) {
/*
* MIGRATE_MOVABLE pcplist could have the pages on CMA area and
* we need to skip it when CMA area isn't allowed.
*/
if (!IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_CMA) || alloc_flags & ALLOC_CMA ||
migratetype != MIGRATE_MOVABLE) {
page = rmqueue_pcplist(preferred_zone, zone, order,
gfp_flags, migratetype, alloc_flags);
goto out;
}
}
/*
* We most definitely don't want callers attempting to
* allocate greater than order-1 page units with __GFP_NOFAIL.
*/
WARN_ON_ONCE((gfp_flags & __GFP_NOFAIL) && (order > 1));
///处理order大于0情况,先获取zone的锁,并关中断
spin_lock_irqsave(&zone->lock, flags);
do {
page = NULL;
/*
* order-0 request can reach here when the pcplist is skipped
* due to non-CMA allocation context. HIGHATOMIC area is
* reserved for high-order atomic allocation, so order-0
* request should skip it.
*/
if (order > 0 && alloc_flags & ALLOC_HARDER) {
///先从当前order链表中去分配page
page = __rmqueue_smallest(zone, order, MIGRATE_HIGHATOMIC);
if (page)
trace_mm_page_alloc_zone_locked(page, order, migratetype);
}
if (!page)
///如果当前order分配失败,从高order的可迁移,可回收链表中查找是否可以借用
page = __rmqueue(zone, order, migratetype, alloc_flags);
} while (page && check_new_pages(page, order));///检查所有分配的页面是否合格
if (!page)
goto failed;
///更新zone统计值NR_FREE_PAGES
__mod_zone_freepage_state(zone, -(1 << order),
get_pcppage_migratetype(page));
///释放锁,恢复中断
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&zone->lock, flags);
__count_zid_vm_events(PGALLOC, page_zonenum(page), 1 << order);
zone_statistics(preferred_zone, zone, 1);
out:
/* Separate test+clear to avoid unnecessary atomics */
///设置了临时水位,唤醒kswapd内核线程回收,当页面分配器触发从备份空闲链表借用内存时,说明已经发生外碎片化了
if (test_bit(ZONE_BOOSTED_WATERMARK, &zone->flags)) {
clear_bit(ZONE_BOOSTED_WATERMARK, &zone->flags);
wakeup_kswapd(zone, 0, 0, zone_idx(zone));
}
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(page && bad_range(zone, page), page);
return page;
failed:
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&zone->lock, flags);
return NULL;
}
参数:
- preferred_zone:首选zone;
- zone:当前遍历的 zone;
- order:申请的物理页面 order;
- gfp_flags:分配掩码
- alloc_flags:分配器内部使用的标志位;
- migratetype:用以指定迁移类型
3.1 rmqueue_pcplist
负责从每 CPU 的 per-cpu 页面列表(PCP,per-cpu pages)中移除内存页面。这个函数通常与伙伴系统的内存分配配合使用,用来减少内存分配时的锁竞争,提升分配性能
static struct page *rmqueue_pcplist(struct zone *preferred_zone,
struct zone *zone, unsigned int order,
gfp_t gfp_flags, int migratetype,
unsigned int alloc_flags)
{
struct per_cpu_pages *pcp;
struct list_head *list;
struct page *page;
unsigned long flags;
local_lock_irqsave(&pagesets.lock, flags);
/*
* On allocation, reduce the number of pages that are batch freed.
* See nr_pcp_free() where free_factor is increased for subsequent
* frees.
*/
pcp = this_cpu_ptr(zone->per_cpu_pageset);
pcp->free_factor >>= 1;
list = &pcp->lists[order_to_pindex(migratetype, order)];
page = __rmqueue_pcplist(zone, order, migratetype, alloc_flags, pcp, list);
local_unlock_irqrestore(&pagesets.lock, flags);
if (page) {
__count_zid_vm_events(PGALLOC, page_zonenum(page), 1);
zone_statistics(preferred_zone, zone, 1);
}
return page;
}
pcp:当前 CPU 对应的per_cpu_pageset,每个 CPU 都有自己的页面池。list:指向当前order和migratetype类型的页面链表。page:分配的页面。flags:用于保存锁的状态。
rmqueue_pcplist 函数通过从每个 CPU 的页面池中移除一个页面来处理内存分配请求。它在获取页面时会对 CPU 级别的页面池进行加锁,减少批量释放的页面数量,以提高分配效率。该函数在分配成功后更新相关的统计信息,并返回分配到的页面。
3.2 处理order>0的分配流程
rmqueue() 函数处理可能有 4 种处理方式:
当order = 0,进入 pcp 的分配流程;
当order > 0,进入以下分配流程:
- 如果alloc_flags 设定了ALLOC_HARDER,migrate type 改 MIGRATE_HIGHATOMIC 进入 __rmqueue_smallest() 函数;
- 如果alloc_flags 没有设定 ALLOC_HARDER 或者经过 MIGRATE_HIGHATOMIC 并没有申请到内存时:
- 如果alloc_flags 设定了 ALLOC_CMA,通过 __rmqueue_cma() 函数改 MIGRATE_CMA 进入 __rmqueue_smallest() 函数;
- 如果alloc_flags 没有设定 ALLOC_CMA 或者经过 CMA 还没有申请page,走原定的migrate 进入 __rmqueue_samllest() 函数;
do {
page = NULL;
/*
* order-0 request can reach here when the pcplist is skipped
* due to non-CMA allocation context. HIGHATOMIC area is
* reserved for high-order atomic allocation, so order-0
* request should skip it.
*/
if (order > 0 && alloc_flags & ALLOC_HARDER) {
///先从当前order链表中去分配page
page = __rmqueue_smallest(zone, order, MIGRATE_HIGHATOMIC);
if (page)
trace_mm_page_alloc_zone_locked(page, order, migratetype);
}
if (!page)
///如果当前order分配失败,从高order的可迁移,可回收链表中查找是否可以借用
page = __rmqueue(zone, order, migratetype, alloc_flags);
} while (page && check_new_pages(page, order));///检查所有分配的页面是否合格
3.2.1 __rmqueue_smallest
static __always_inline
struct page *__rmqueue_smallest(struct zone *zone, unsigned int order,
int migratetype)
{
unsigned int current_order;
struct free_area *area;
struct page *page;
/* Find a page of the appropriate size in the preferred list */
///从order开始,向上查找
for (current_order = order; current_order < MAX_ORDER; ++current_order) {
area = &(zone->free_area[current_order]);
page = get_page_from_free_area(area, migratetype);
if (!page)
continue;
///分配成功,将page从free_list删除
del_page_from_free_list(page, zone, current_order);
///实现分配page,current_order > order
///多余pages,放回伙伴系统
expand(zone, page, order, current_order, migratetype);
set_pcppage_migratetype(page, migratetype);
return page;
}
return NULL;
}
- 从当前申请的 order 往 MAX_ORDER 方向寻找 free_area 有空闲页的free list,如果当前order 对应的 migratetype 没有空闲页,则往上一级order查询;
- 若查询到了page,先通过 del_page_from_free_area() 函数从free list 中移除。
- 然后通过 expand() 分配,只把需要的 order 分配出来,其他的剩余部分再添加到其他 order 的free list
- 如果轮询了 free_area 所有order,则返回NULL,标记此次分配存在内存紧缺,返回到上一级尝试其他的分配方式
下面对这几个函数详细解析一下
- del_page_from_free_area
static inline void del_page_from_free_list(struct page *page, struct zone *zone,
unsigned int order)
{
/* clear reported state and update reported page count */
if (page_reported(page))
__ClearPageReported(page);
list_del(&page->lru);
__ClearPageBuddy(page);
set_page_private(page, 0);
zone->free_area[order].nr_free--;
}
- 清除 PG_buddy 的标记;
- 清除 page->private 的order 印记;
- area->nr_free 对应的页块数量减 1;
- expand
///多余的内存,放回伙伴系统,high>low
static inline void expand(struct zone *zone, struct page *page,
int low, int high, int migratetype)
{
unsigned long size = 1 << high;
while (high > low) {
high--;
size >>= 1;
VM_BUG_ON_PAGE(bad_range(zone, &page[size]), &page[size]);
/*
* Mark as guard pages (or page), that will allow to
* merge back to allocator when buddy will be freed.
* Corresponding page table entries will not be touched,
* pages will stay not present in virtual address space
*/
///设置page_guard
if (set_page_guard(zone, &page[size], high, migratetype))
continue;
///“切一半”,加入对应free_list链表中
add_to_free_list(&page[size], zone, high, migratetype);
///设置buddy标记
set_buddy_order(&page[size], high);
}
}
主要是将该页块进行切割,将高地址的一半放置在低一级的 area 对应的 migratetype 中,将低地址的页块继续切割,一直切割到所需要的 order 为止。
add_to_free_area() 在将页块放置到 area 的同时,也会将该 area->nr_free 计数加1;
set_page_order() 主要设置page->private 为对应的order,并标记页块的 PG_buddy;
3.3 wakeup_kswapd
///设置了临时水位,唤醒kswapd内核线程回收,当页面分配器触发从备份空闲链表借用内存时,说明已经发生外碎片化了
if (test_bit(ZONE_BOOSTED_WATERMARK, &zone->flags)) {
clear_bit(ZONE_BOOSTED_WATERMARK, &zone->flags);
wakeup_kswapd(zone, 0, 0, zone_idx(zone));
}
在 rmqueue() 函数的最后会判断 zone->flags 是否指定了 ZONE_BOOSTED_WATERMARK,来确定是否唤醒 kswapd 线程。
注意, 这里通过函数 wakeup_kswapd() 只唤醒当前 zone 的kswapd 进行扫描回收内存,其他zone 并不唤醒扫描。
